Multi-mode & Single-mode Fibre Optic Cable
Fiber Optic Cables Construction
There are several types of
fiber optic cables, and they are differentiated according many construction properties like the core, buffer, fiber count, cable arrangement, sub units, filling, strength member, and outer jacket. Mixing all these properties, with each having its own derivative options, results in a large variety of fiber optical cables that can be used for different applications.
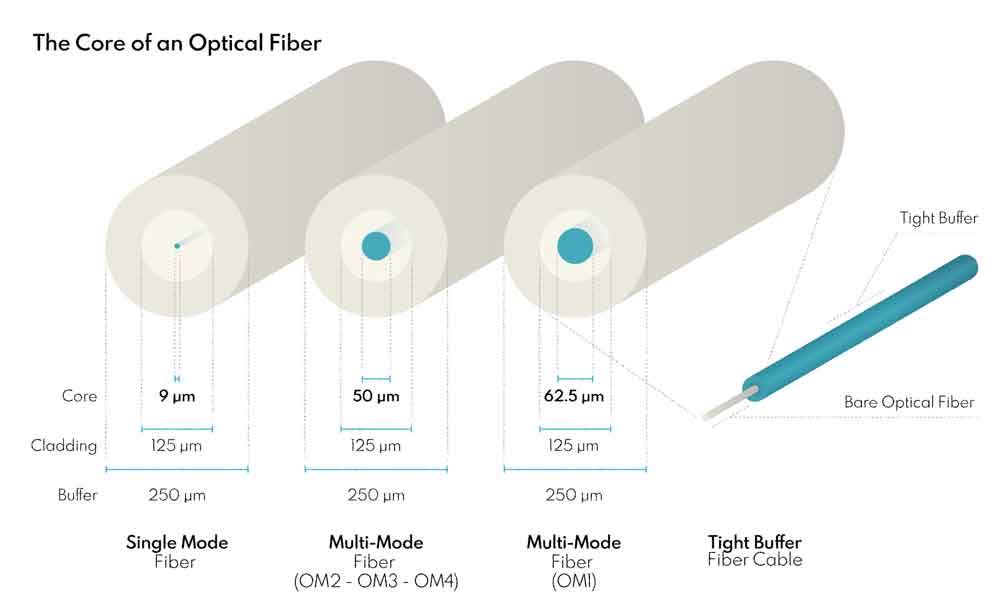
Fiber Optic Cable Construction PropertiesThe diameter of the inner “Core” of a fiber strand defines the main usage of a fiber cable. A fiber with a 9µm (9 micrometer) diameter core allows only one single light pulse to pass through it at a time, thus it is called
single mode fiber.
On the other hand, a fiber with a 62.5µm or 50µm core diameter, allows for multiple pulses of light to refract and pass through it; and this type is called multi-mode fiber. Single mode fibers have a longer range but only transfer one signal; a single mode fiber can transfer one light signal up to 5 kilometers. Oppositely, multi-mode fibers can transfer several signals at the same time but to a shorter range; a multi-mode fiber can transfer multiple light signals up to 550 meters.
| Fiber Optic Cable Construction Properties Fiber Core and Cladding |
Single Mode |
Multi-mode |
| Fibers Count |
Simplex |
Duplex or Multiple |
| Cable Arrangement |
Tight Buffer |
Loose Tube |
| Sub Units |
Cord Cable |
Breakout Cable |
| Cable Filling |
Gel-free |
Gel-filled |
| Strength Member |
Aramid Yarn |
Glass Yarn |
| Cable Coating Jacket |
Indoor Safe |
Outdoor Resistant |
Multi-mode OM1 fibre optic cable (62.5/125)
Multi-mode OM1 fibre optic cable has 62.5/125µm cores and is generally used for backbone applications due to high capacity and reliability.
Loose tube versions are ideal for external use and commonly available with SWA or
CST mechanical protection. Tight buffered versions are designed for runs around multiple bends and not usually armoured.
Multi-mode fibres have larger core diameters than single-mode so the light is reflected in a zigzag pattern down the core, resulting in higher attenuation rates (losses) than single-mode.
Construction – Multi-mode OM1 fibre
- 1. 62.5/125µm fibres with coloured coating
- 2. fibres are either contained in a loose tube (LT) or tight buffered (TB)
- 3. optional steel wire armour (SWA) or corrugated steel tape armour (CST)
- 4. generally with low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) sheathing
Technical – Multi-mode OM1 fibre
- 1. fibre diameter:core 62.5µm (micrometres), cladding 125µm
- 2. number of fibres:4, 6, 8, 12, 16 or 24 core versions commonly available
- 3. loose tube (LT):fibres are enclosed within protective tube(s), usually with a water resistant gel
- 4. tight buffered (TB):fibres have an additional tough waterproof layer over the normal coating
Multi-mode OM2 OM3 or OM4 fibre optic cable (50/125)
Construction – Multi-mode OM2, OM3 or OM4 fibre optic
- 1. 50/125µm fibres with coloured coating
- 2. fibres are either contained in a loose tube (LT) or tight buffered (TB)
- 3. optional steel wire armour (SWA) or corrugated steel tape armour (CST)
- 4. generally with low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) sheathing
Technical – Multi-mode OM2, OM3 or OM4 fibre optic
- 1. fibre diameter:core 50µm (micrometres), cladding 125µm
- 2. number of fibres:4, 6, 8, 12, 16 or 24 core versions commonly available
- 3. loose tube (LT):fibres are enclosed within protective tube(s), usually with a water resistant gel
- 4. tight buffered (TB):fibres have an additional tough waterproof layer over the normal coating
Single-mode OS1 or OS2 fibre optic cable (9/125)
Single-mode OS1 or OS2 fibre optic cable has 9/125µm cores and is commonly utilized where low attenuation rates are required over long distances. Loose tube versions are ideal for external use and commonly available with SWA or CST mechanical protection. Tight buffered versions are designed for runs around multiple bends and not usually armoured.
Single-mode fibres have much smaller core diameters than multi-mode so the light does not reflect as often, reducing losses to a minimum and guaranteeing an enormous range.
Construction – Single-mode OS1 or OS2 fibre optic
- 1. 9/125µm fibres with coloured coating
- 2. fibres are either contained in a loose tube (LT) or tight buffered (TB)
- 3. optional steel wire armour (SWA) or corrugated steel tape armour (CST)
- 4. generally with low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) sheathing
Technical – Single-mode OS1 or OS2 fibre optic
- 1. fibre diameter: core 9µm (micrometres), cladding 125µm
- 2. number of fibres: 4, 6, 8, 12, 16 or 24 core versions commonly available
- 3. loose tube (LT): fibres are enclosed within protective tube(s), usually with a water resistant gel
- 4. tight buffered (TB): fibres have an additional tough waterproof layer over the normal coating
For a closer look at
Multimode & Singlemode Fiber Optic Cable Price, you can check this website, and do not hesitate to email us for more info on
info@uni-fibercable.com
How to Order OFC Cable Price
Our team is committed to providing outstanding service before, during, and after the sale. To learn more about our products or to place an order, please contact your sales representative. WhatsApp/Mobile/WeChat our Customer Service Department at
+86 186 3866 8721 or email us at
info@uni-fibercable.com
